When it comes to fluid handling in various industries, the choice of pump can significantly affect efficiency, cost, and maintenance. Among the many types of pumps available, progressive cavity pumps and jet pumps are two popular options, each with its unique advantages and limitations. This article will compare these two types of pumps, highlighting their key features, applications, and operational mechanisms.

Overview of Progressive Cavity Pumps
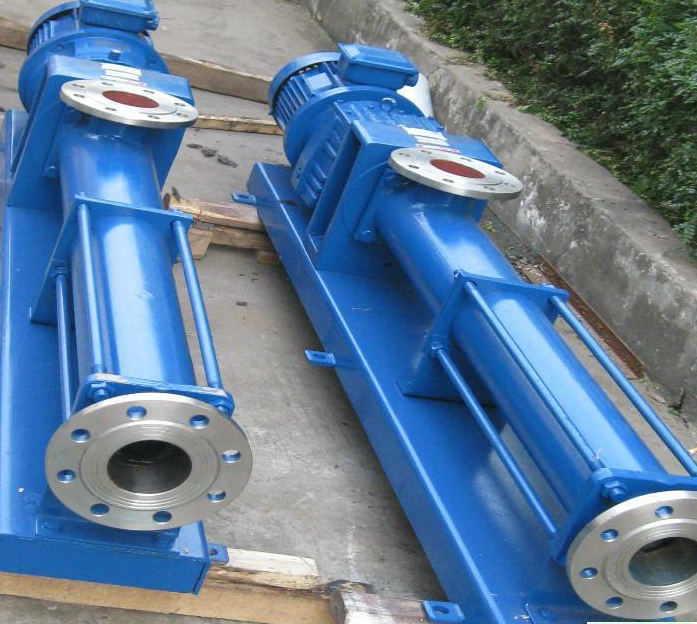
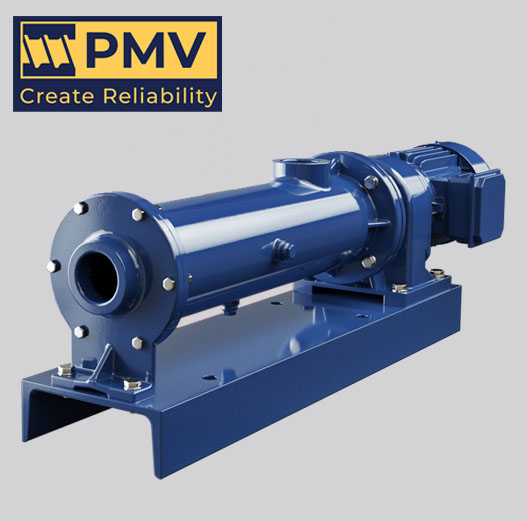
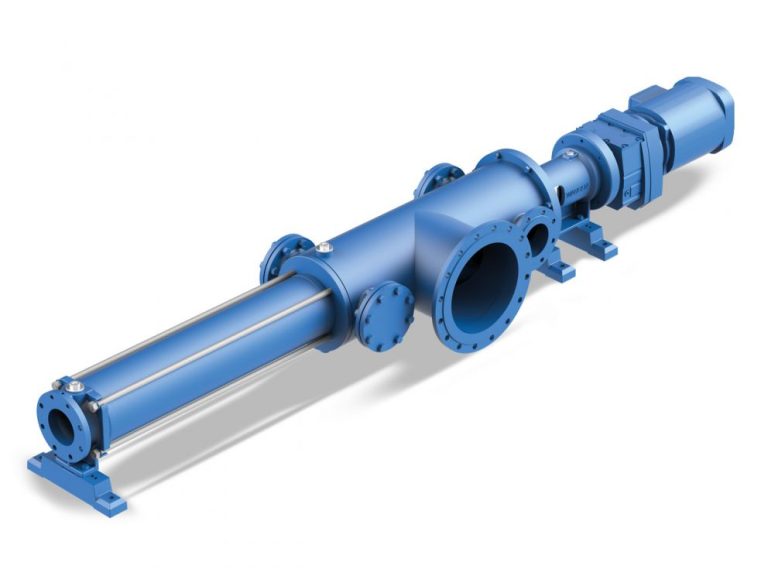
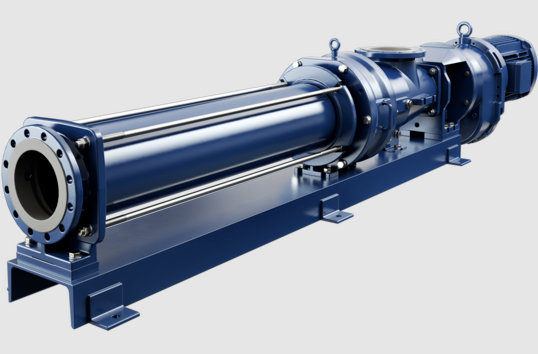
Progressive cavity pumps, also known as helical rotor pumps, are positive displacement pumps that use a rotating screw-like rotor within a stator to move fluids. This design allows for a smooth and continuous flow, making them suitable for various applications.
Key Features:
- Continuous Flow: They provide a steady flow rate regardless of pressure changes.
- Versatility: Effective for handling a wide range of viscous fluids, including slurries and emulsions.
- Low Shear: Gentle pumping action preserves the integrity of sensitive fluids.
Applications:
- Food and Beverage: Used for transferring viscous materials like yogurt and sauces.
- Chemical Processing: Ideal for pumping corrosive or abrasive fluids.
- Wastewater Management: Effective for moving sludge and other thick materials.
Overview of Jet Pumps
Jet pumps, on the other hand, operate on a different principle. They utilize a high-velocity jet of fluid to create a vacuum, which draws in and mixes additional fluid. This design is commonly used for applications requiring lower flow rates and can handle a variety of fluids.
Key Features:
- Simplicity: Fewer moving parts result in lower maintenance requirements.
- Self-Priming: Can operate in situations where other pumps may struggle due to air in the line.
- Cost-Effective: Generally lower initial investment compared to progressive cavity pumps.
Applications:
- Water Supply: Often used in residential and agricultural settings for well water extraction.
- Cooling Systems: Effective in circulating fluids in industrial cooling applications.
- Chemical Injection: Commonly used for injecting chemicals into water streams.
Comparison of Operational Mechanisms
- Pumping Action:
- Progressive cavity pumps utilize a mechanical rotor-stator arrangement for fluid movement.
- Jet pumps rely on fluid dynamics to create a vacuum that draws in additional fluid.
- Flow Characteristics:
- Progressive cavity pumps achieve a constant flow rate, making them suitable for precise applications.
- Jet pumps may experience fluctuations in flow based on the suction conditions.
- Viscosity Handling:
- Progressive cavity pumps excel in handling high-viscosity fluids.
- Jet pumps are more limited in their ability to handle viscous materials.
Conclusion
Both progressive cavity pumps and jet pumps have their distinct advantages and are suited for different applications. While progressive cavity pumps offer versatility and continuous flow for viscous materials, jet pumps provide a cost-effective and simpler solution for lower flow applications. Choosing the right pump ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application, including fluid characteristics, desired flow rates, and maintenance considerations. Understanding these differences can help industries make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and performance.
People also ask
Send Your Enquiry :