Pump Screw-PMV Pump
People Also Ask
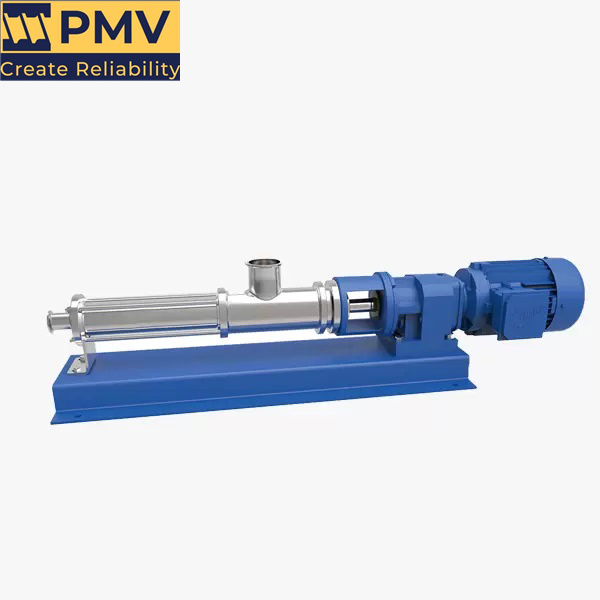
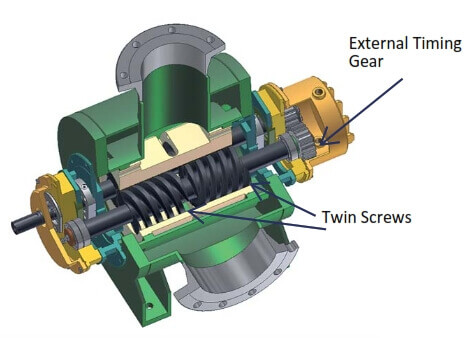
Rotary screw pumps are a type of positive displacement pump that uses two helical screws to move fluids. They are known for their efficiency and ability to handle a wide range of viscosities, making them suitable for various applications. Here’s a breakdown of their key characteristics, working principles, and applications.

People Also Ask
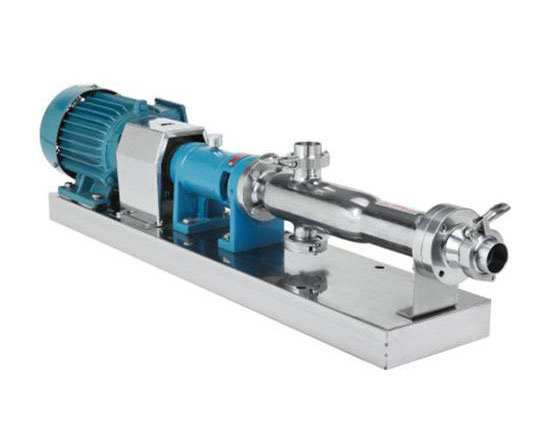

Sanitary Screw Pump Efficient and Hygienic Liquid Transfer Made Easy with Sanitary Screw Pumps Brief description: The sanitary screw pump meets the sanitary standards and is made of polished stainless steel. It can be customized with a cart funnel. It can transport a wide range of liquids with different types and viscosities. It can be…
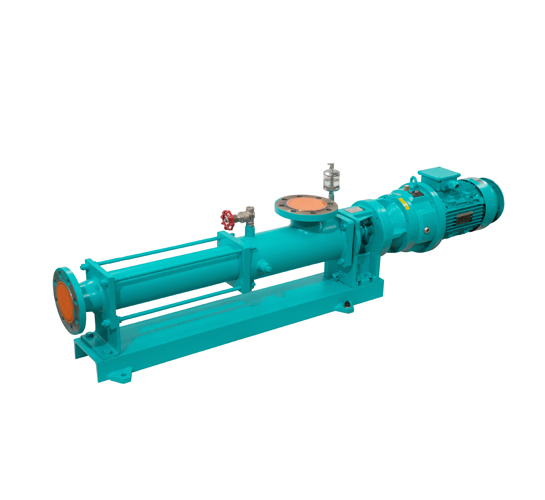

Single Screw pump What is single screw pump? Single screw pump is a type of rotary positive displacement pump that operate according to the positive displacement principle. Single screw pump working principle is based on the interaction between a single-helix metal rotor and a double-helix elastic stator, which creates sealed cavities that move fluid from…