-
-
-
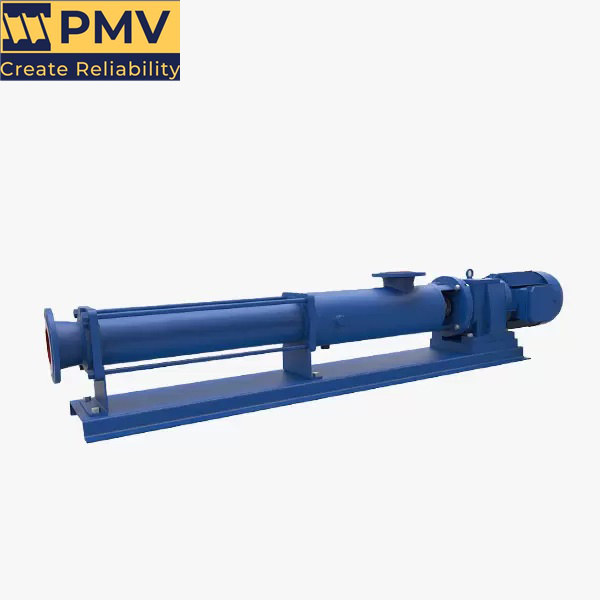
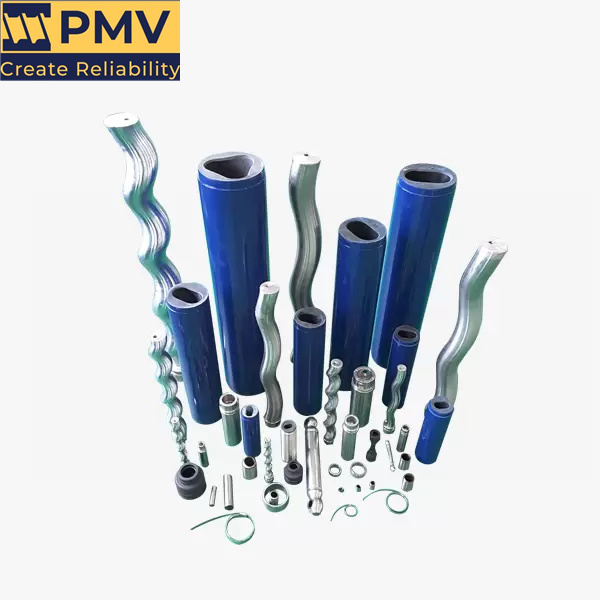
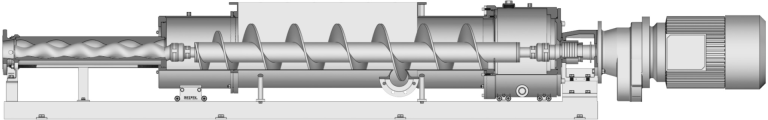
Pump Screw-PMV Pump
People Also Ask
-
-
-
-
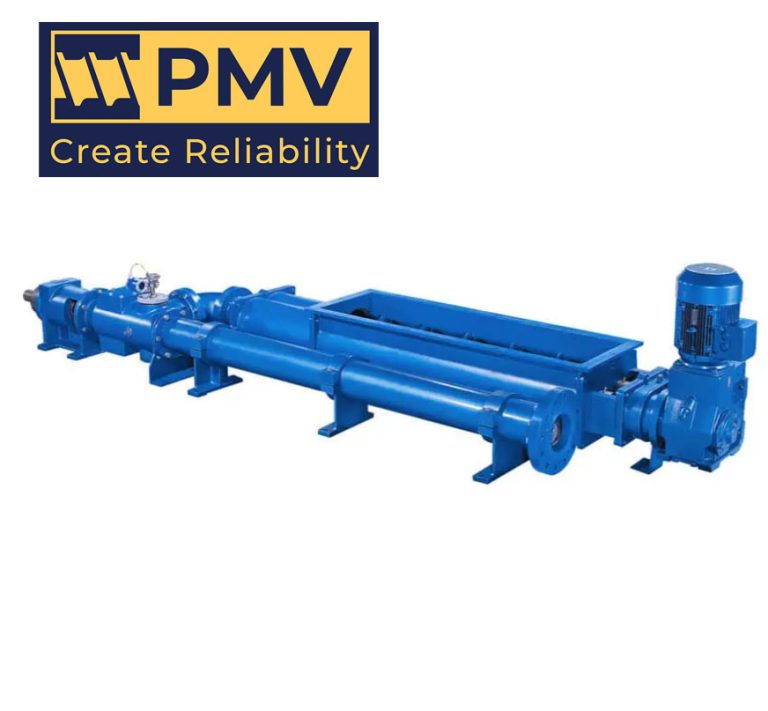
PMV Progressing Cavity Pump Manufacturers
What is PMV Progressing Cavity Pumps Manufacturers? PMV Pump Manufacture Co., Ltd was founded in 2003, is a professional pump enterprise integrating research, development, production, sales and service. Since its inception, quality management has always been the first goal. Therefore, we have designated staff responsible for raw material composition inspection, pump case bulge test, performance…
-
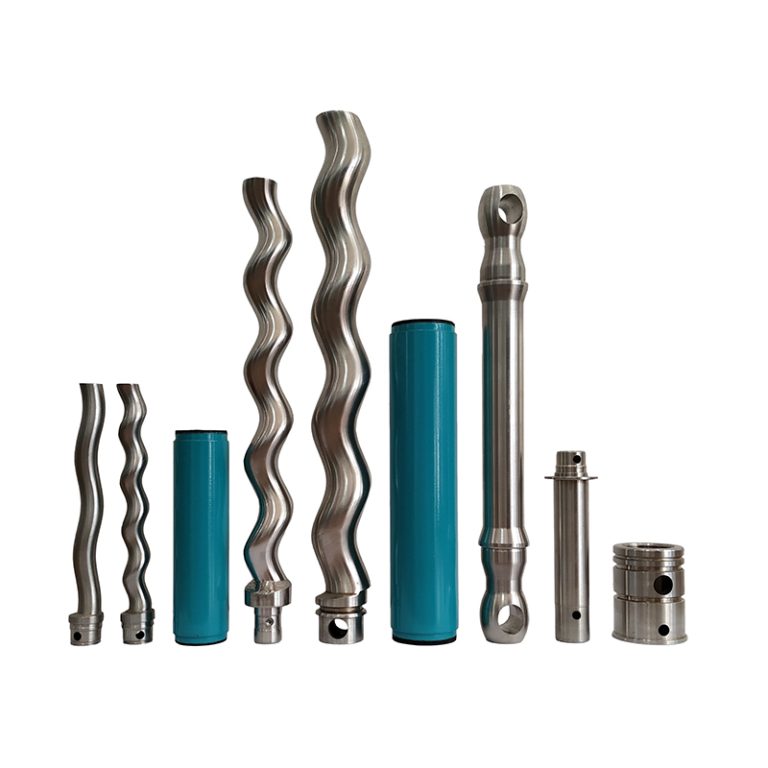
Type of Screw Pump-Pumpvv
What is a screw pump? Screw pump is a part of the dry compressed gas transfer pump series. They are positive displacement pumps that use one or more screws to move fluid or water along the screw shaft. These screws interlock to pressurize the fluid and move it into the system. These screws engage each…
-
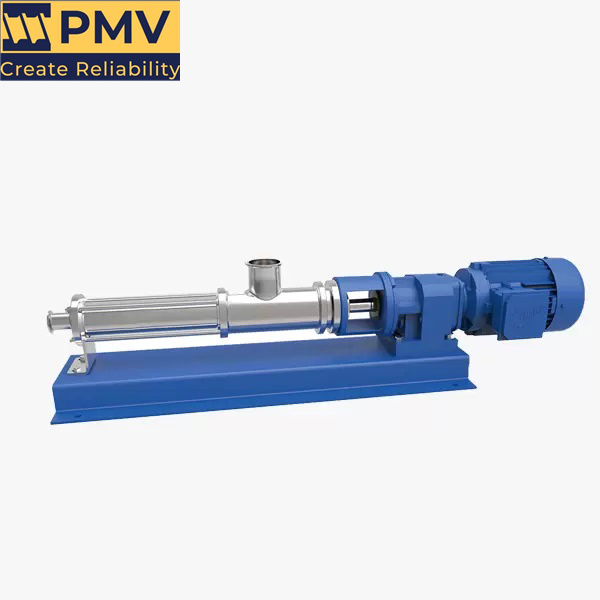
Screw Pump-Pumpvv
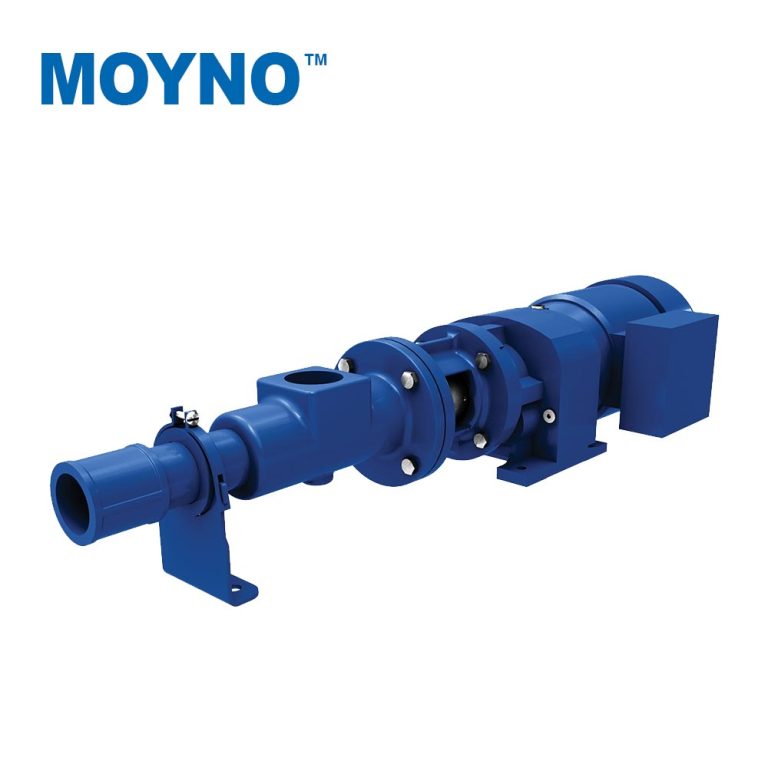
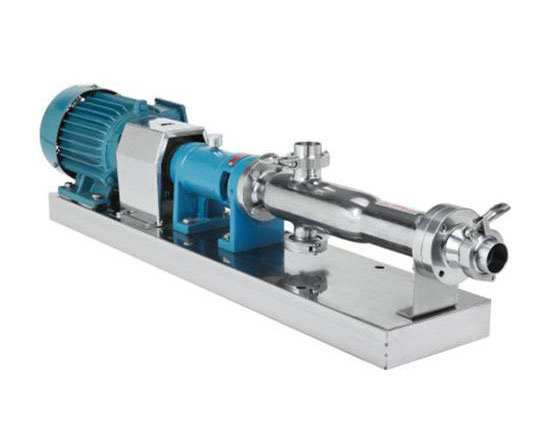
The Description of Screw Pump A screw pump is a type of positive displacement pump that utilizes an intermeshing screw and housing to transfer fluids or viscous substances. The pump consists of two or more screws (also known as rotors) that rotate in opposite directions, creating chambers that trap and move the fluid along the…
-
Screw Pump Diagram
Introduction to Screw Pump Diagram. A screw pump diagram is a schematic representation of the working principle and components of a screw pump. Screw pumps are positive displacement pumps that use rotating screws to move fluids or slurries through a system. They are widely used in various industries due to their ability to handle high…
screw pump working
Screw pumps are a type of positive displacement pump that employs one or more screws to move fluids. They are known for their ability to handle a wide range of viscosities and provide a smooth flow. Here’s a comprehensive overview of how screw pumps work:
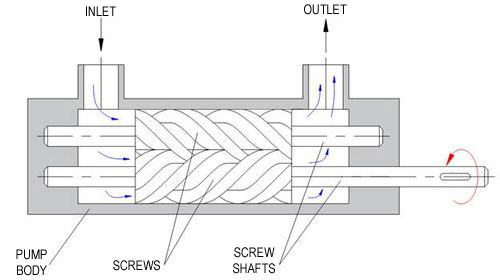
1. Basic Components of a Screw Pump
-
- Screws:
-
- Typically consists of one or more helical screws (rotors) that rotate in a casing.
-
- Casing:
-
- The outer housing that contains the screws and directs the fluid flow.
-
- Inlet and Outlet Ports:
-
- Openings for fluid entry (inlet) and exit (outlet) from the pump.
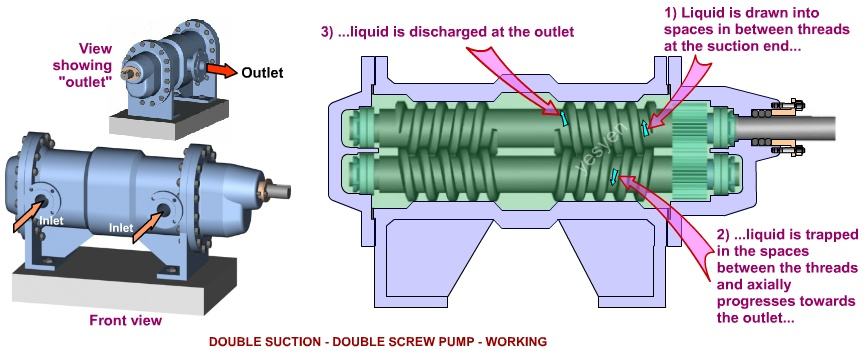
2. Working Principle
A. Fluid Entry
-
- Inlet Suction:
-
- As the screws rotate, they create a vacuum at the inlet, drawing fluid into the pump.
B. Fluid Transport
-
- Screw Rotation:
-
- The rotating screws move the fluid along the length of the screws.
-
- Positive Displacement:
-
- The design ensures that the fluid is trapped between the screws and the casing, creating a continuous flow.
C. Fluid Displacement
-
- Flow Direction:
-
- As the screws turn, the fluid is pushed towards the outlet port, maintaining a steady flow rate.
-
- Pressure Generation:
-
- The continuous movement of the screws generates pressure, allowing the fluid to exit the pump.
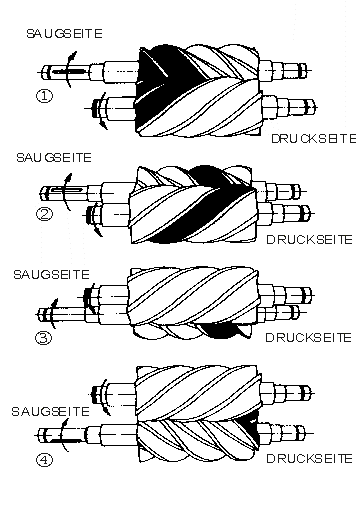
3. Types of Screw Pumps
-
- Single-Screw Pumps:
-
- Features a single rotor and a stationary casing, often used for low-viscosity fluids.
-
- Twin-Screw Pumps:
-
- Comprises two intermeshing screws that enhance efficiency and are suitable for a wide range of viscosities.
-
- Triple-Screw Pumps:
-
- Incorporates three screws and provides high efficiency and pressure generation, typically used in high-performance applications.
4. Advantages of Screw Pumps
-
- Smooth Flow:
-
- Produces a continuous and smooth flow with minimal pulsation, making them ideal for sensitive applications.
-
- Versatility:
-
- Capable of handling various fluids, including viscous, abrasive, and shear-sensitive materials.
-
- Self-Priming:
-
- Many screw pumps can self-prime, eliminating the need for external priming systems.
-
- Low Maintenance:
-
- Fewer moving parts compared to other pump types, resulting in reduced maintenance requirements.
5. Applications of Screw Pumps
-
- Oil and Gas:
-
- Used for transporting crude oil and other petroleum products.
-
- Chemical Processing:
-
- Suitable for handling various chemicals and corrosive fluids.
-
- Food and Beverage:
-
- Employed for pumping food products, such as syrups and oils, without damaging them.
-
- Wastewater Treatment:
-
- Utilized for moving sludge and other viscous materials in treatment plants.