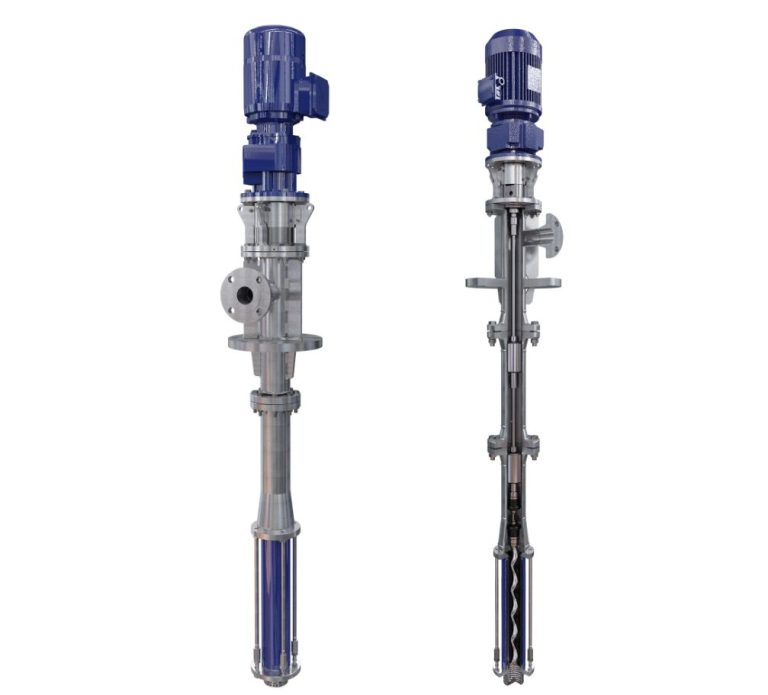
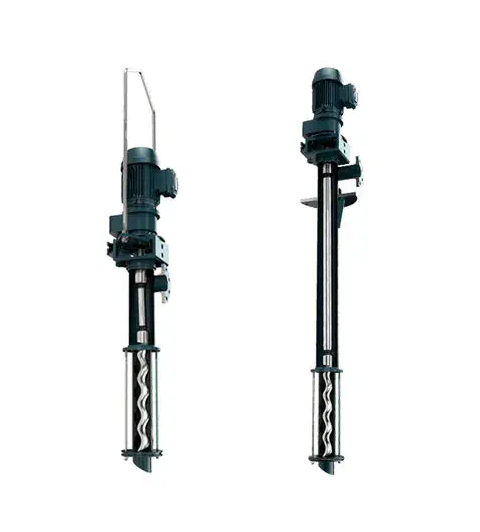
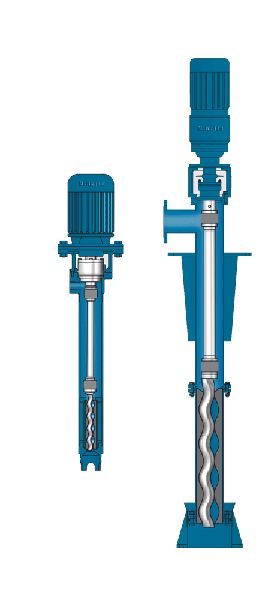
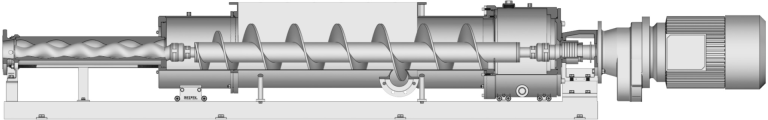
PCM MOINEAU™ AV VERTICAL PROGRESSING CAVITY PUMPS
PCM VERTICAL PROGRESSING CAVITY PUMPS The PCM Moineau™ AV vertical progressing cavity pump is the ideal solution for upstream and downstream oil & gas applications within onshore and offshore facilities. It combines API standards with our unrivalled industry expertise. MOINEAU™ PROGRESSING CAVITY CRUDE OIL TRANSFER PUMPS Founder of the PCM company in 1932, René Moineau…