Introduction
Progressive cavity pumps are widely used in various industries for their ability to handle viscous fluids and maintain a steady flow. One important aspect of their operation is the concept of Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH), which plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient performance of these pumps.
Understanding NPSH
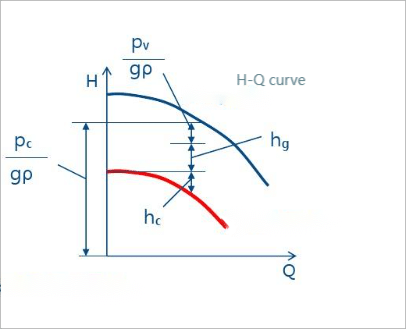
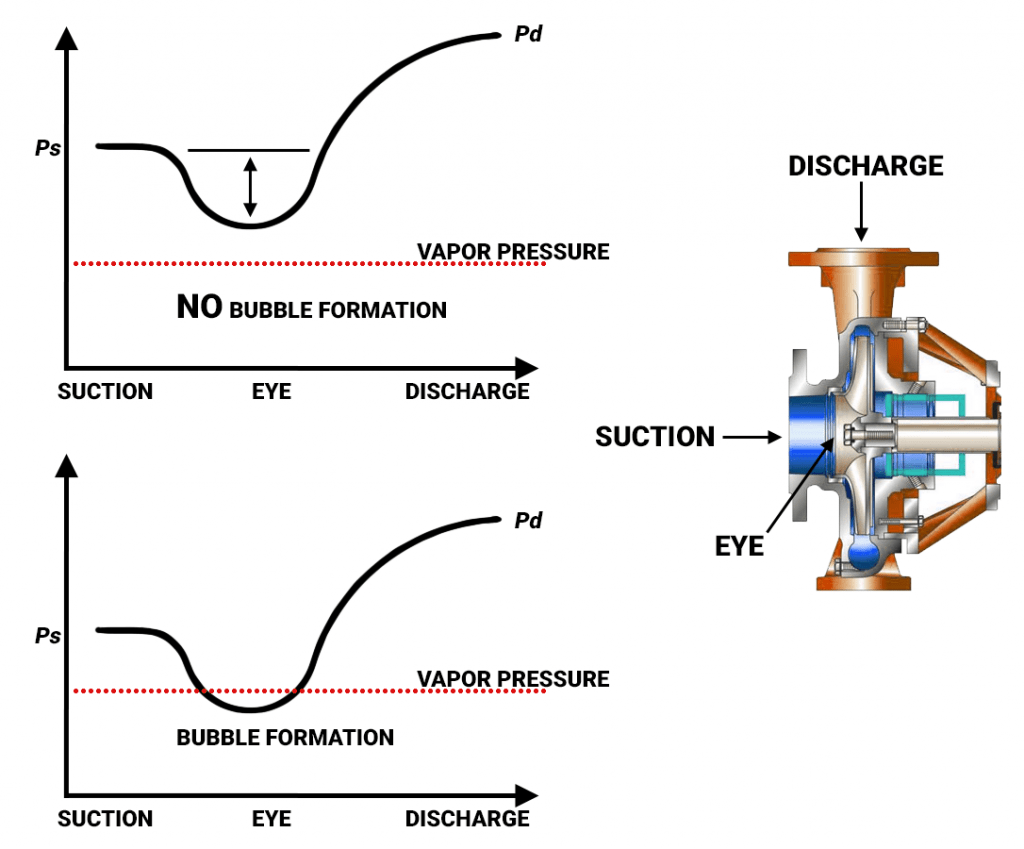
NPSH is a measure of the pressure available at the pump inlet to prevent cavitation. Cavitation occurs when the pressure in the pump drops below the vapor pressure of the fluid, leading to the formation of vapor bubbles. These bubbles can collapse violently, causing damage to the pump components and reducing efficiency.
Types of NPSH
- NPSH Available (NPSHa): This is the actual pressure available at the pump suction. It takes into account the atmospheric pressure, the fluid’s elevation, and the pressure losses associated with the piping system.
- NPSH Required (NPSHr): This is the minimum pressure required at the pump suction to prevent cavitation, determined by the pump manufacturer based on the design and operating conditions.
Importance of NPSH
- Prevention of Cavitation: Ensuring that NPSHa exceeds NPSHr is essential to prevent cavitation, which can lead to severe pump damage and operational issues.
- Efficiency: Proper NPSH levels contribute to the pump’s overall efficiency, allowing for consistent and reliable fluid transfer.
- Longevity: Maintaining appropriate NPSH conditions helps extend the lifespan of the pump by reducing wear and tear from cavitation damage.
Factors Affecting NPSH
Several factors can influence the NPSH available to a progressive cavity pump:
- Fluid Characteristics: Viscosity and temperature of the fluid can significantly affect the NPSH.
- Pump Design: The specific design of the pump, including its materials and configuration, determines the NPSHr.
- Piping System: The layout and diameter of the suction piping, as well as the presence of bends and fittings, can cause pressure losses that impact NPSHa.
Best Practices for Managing NPSH
To ensure optimal performance of progressive cavity pumps, consider the following best practices:
- Sizing the Pump Correctly: Choose a pump that is appropriately sized for the application to ensure sufficient NPSH.
- Minimizing Suction Lift: Keep the suction lift as low as possible to enhance NPSHa.
- Using Proper Piping: Select an appropriate diameter and minimize bends in the suction piping to reduce pressure losses.
- Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine inspections and maintenance to identify and address potential issues that may affect NPSH.
Conclusion
The NPSH of progressive cavity pumps is a critical factor in their performance and reliability. By understanding the concepts of NPSHa and NPSHr, and by implementing best practices, operators can ensure efficient and long-lasting pump operation. Proper management of NPSH not only prevents cavitation but also enhances the overall efficiency of fluid transfer processes in various industrial applications.
People also ask
Send Your Enquiry :






