[wpseo_breadcrumb]
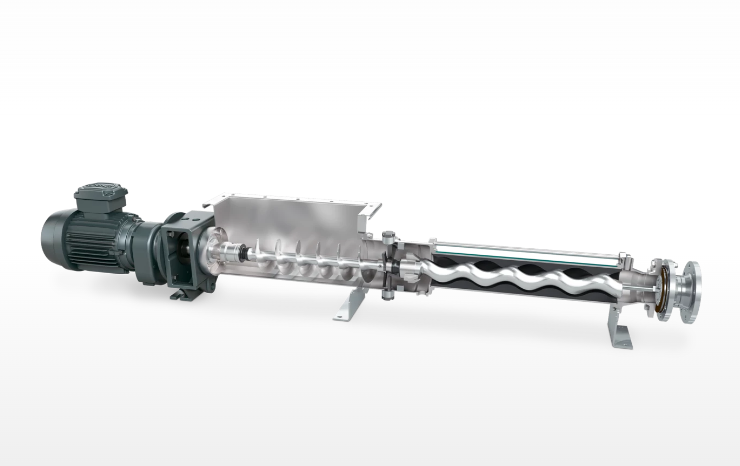
A pump cover is a critical structural and functional component mounted on the shell of various fluid pumps, serving as a key barrier between the pump’s internal core mechanisms and the external environment. Its design and material selection are tailored to the pump’s application scenarios, medium characteristics, and operating pressure, directly impacting the pump’s sealing performance, service life, and operational safety.
Core Functions of the Pump Cover.
The pump cover has three core functions:
- Sealing Protection.
The primary function of the pump cover is to seal the pump chamber tightly, preventing leakage of the conveyed medium (such as water, oil, chemical fluids, etc.). It collaborates with sealing gaskets or mechanical seals to maintain the internal pressure stability of the pump and avoid environmental pollution or resource waste caused by medium leakage. - Internal Component Guard.
It shields the pump’s core internal parts—including impellers, shafts, bearings, and valves—from dust, debris, and other external contaminants. This protection reduces wear and tear on internal components and lowers the risk of operational failures. - Maintenance Accessibility
As a detachable part of the pump body, the pump cover enables convenient disassembly and assembly during maintenance. Technicians can remove the pump cover to inspect, repair, or replace worn internal components without disassembling the entire pump, significantly improving maintenance efficiency.
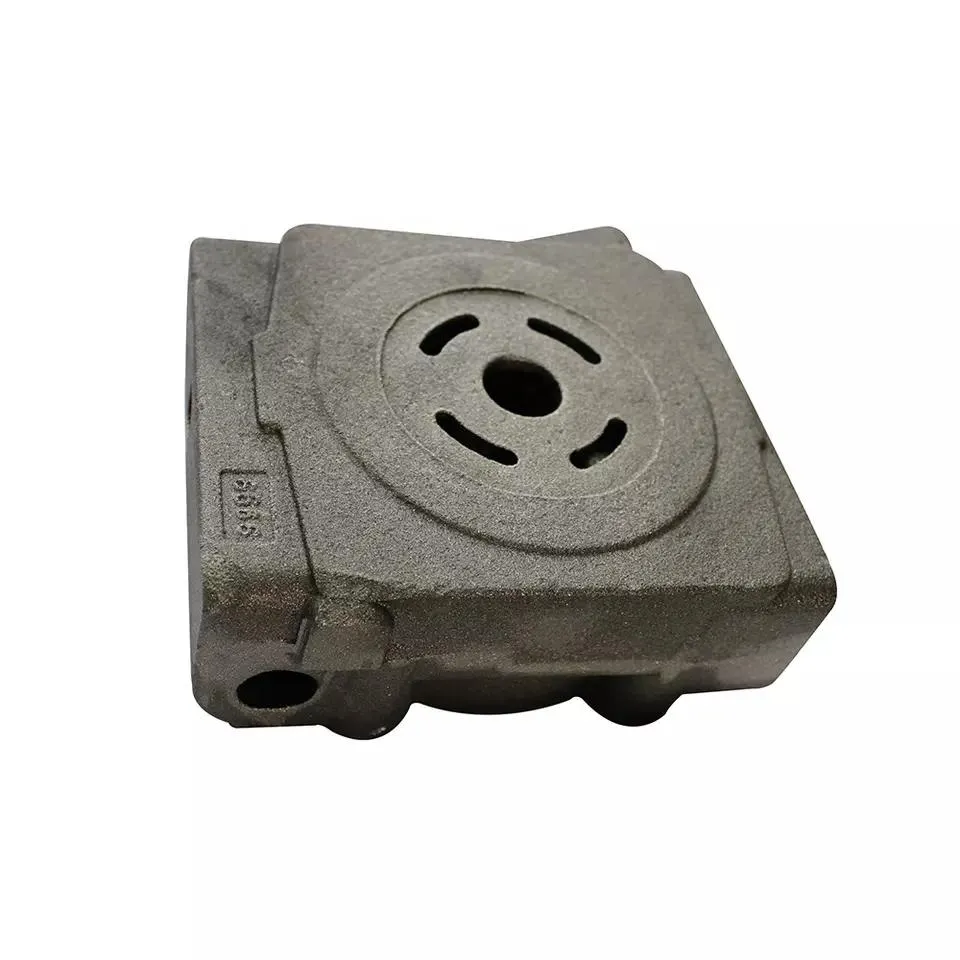


Material Selection Criteria for Pump Covers.
The choice of pump cover material depends on the properties of the conveyed medium and working conditions, with common options including:
- Cast Iron: Cost-effective and durable, suitable for pumps handling non-corrosive media (e.g., clean water, lubricating oil) in low-to-medium pressure environments, such as sump pumps and oil transfer pumps.
- Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316): Excellent corrosion and rust resistance, ideal for chemical pumps, food-grade pumps, or marine pumps that convey corrosive liquids, acidic/alkaline solutions, or hygienic-grade media.
- Engineering Plastic (e.g., PP, PTFE): Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-efficient, applied to small-sized pumps like condensate pumps or household water pumps that handle weak corrosive media.
- Aluminum Alloy: Features high strength-to-weight ratio and good thermal conductivity, suitable for lightweight, high-speed operating pumps such as automotive fuel pump covers, balancing the requirements of structural rigidity and equipment miniaturization.
Application Scope.
Pump covers are essential components for almost all types of pumps, with typical applications including:
- Industrial pumps: High pressure fuel pumps, oil transfer pumps, chemical process pumps.
- Building services pumps: Sump pumps, condensate pumps for HVAC systems.
- Automotive pumps: Engine fuel pump covers, lubricating oil pump covers.
- Household pumps: Portable water pump covers, garden irrigation pump covers.
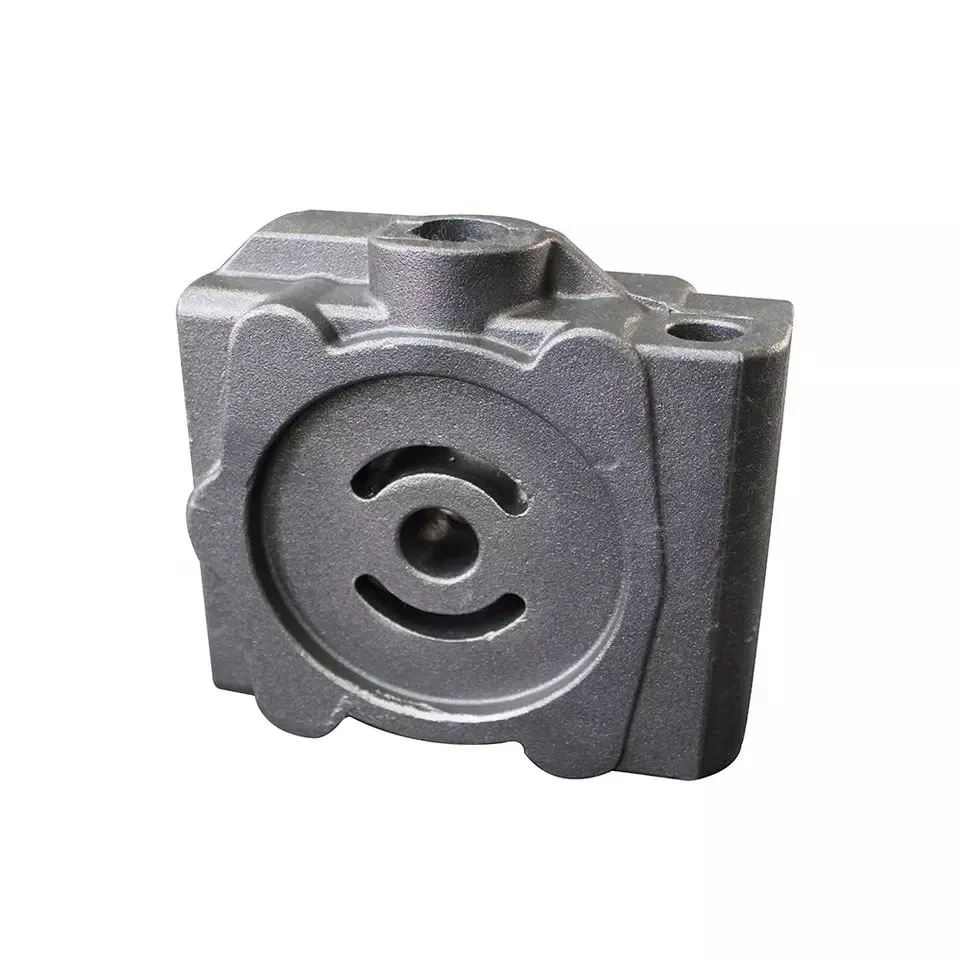

Positive Displacement Pump Cover vs Centrifugal Pump Cover.
| Comparison Dimension | Positive Displacement Pump Cover | Centrifugal Pump Cover |
|---|---|---|
| Core Working Principle Adaptation | Matches the discontinuous fluid trapping & displacement mode, withstands periodic pressure pulsations | Adapts to the continuous centrifugal fluid acceleration mode, bears stable radial pressure |
| Pressure Resistance Performance | Designed for high working pressure (tens to hundreds of MPa); thickened structure with reinforced ribs | Suitable for medium-low pressure (usually ≤ 10 MPa); lightweight structure without excessive reinforcement |
| Material Selection | High-strength ductile cast iron, forged carbon steel, 316L stainless steel; surface hardening treatment optional | Ordinary cast iron, aluminum alloy, engineering plastic (for low-pressure scenarios) |
| Sealing Solution | Metal C-ring seals, spiral wound gaskets, double mechanical seals; focuses on dynamic sealing for pressure fluctuations | Rubber gaskets (NBR/EPDM), single mechanical seals; focuses on static sealing for stable pressure |
| Bolt Configuration | Symmetrically arranged high-grade bolts (Grade 8.8/10.9); strict torque control to ensure uniform stress | Ordinary bolts (Grade 4.8/5.6); lower torque requirements |
| Integrated Functional Interfaces | Integrated pressure relief valve ports, pressure gauge ports, exhaust ports to optimize operation & maintenance | Simple structure with few integrated interfaces; only basic connection ports |
| Sealing Surface Machining Precision | Ultra-high precision (surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.8 μm) via lapping/grinding; critical for volumetric efficiency | Medium precision (surface roughness Ra ≤ 1.6 μm) via turning/milling; meets basic sealing needs |
| Maintenance Design | Detachable independent structure; direct access to internal components (gears/pistons) without full pump disassembly | Often integrated with pump body; requires partial pipeline disassembly for internal maintenance |
| Typical Application Scenarios | Hydraulic gear pumps, piston pumps for oil transportation, chemical screw pumps | Water supply centrifugal pumps, HVAC condensate pumps, household garden pumps |