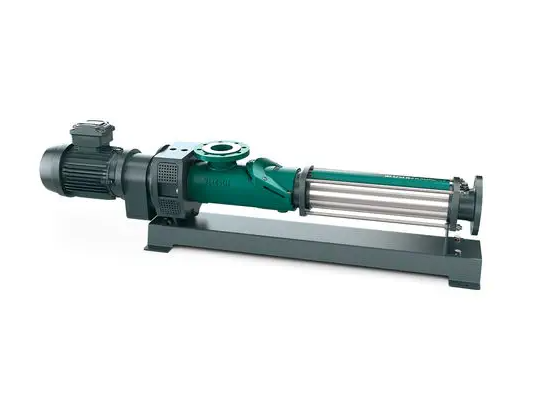
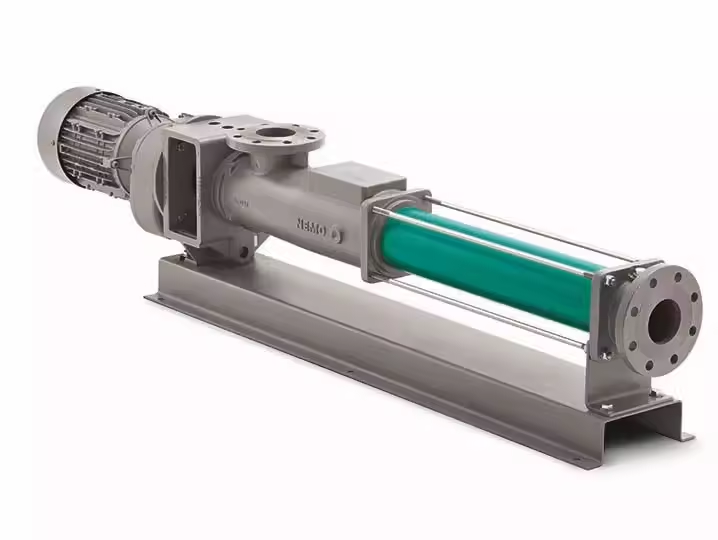
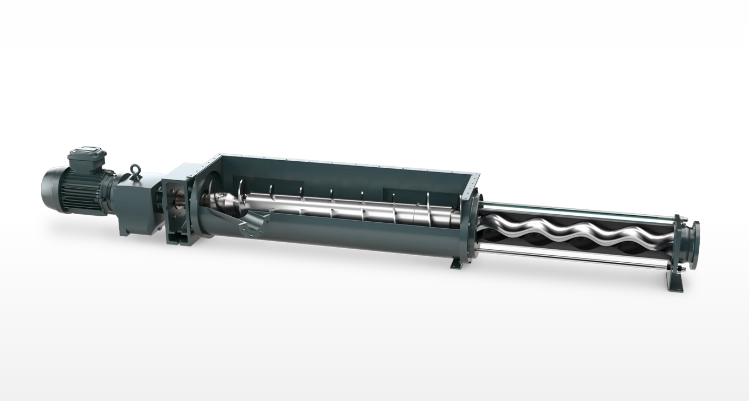
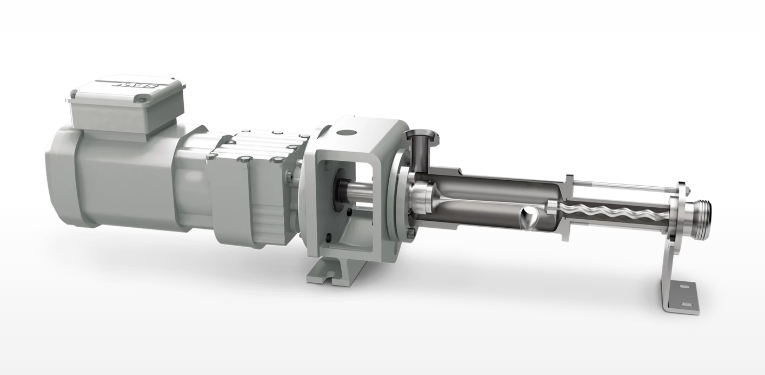
Stator design:
The stator is made of highly wear-resistant polyurethane
The stator has excellent sealing performance to prevent leakage and contamination
The inner wall of the stator is smooth, which is conducive to unimpeded fluid transportation
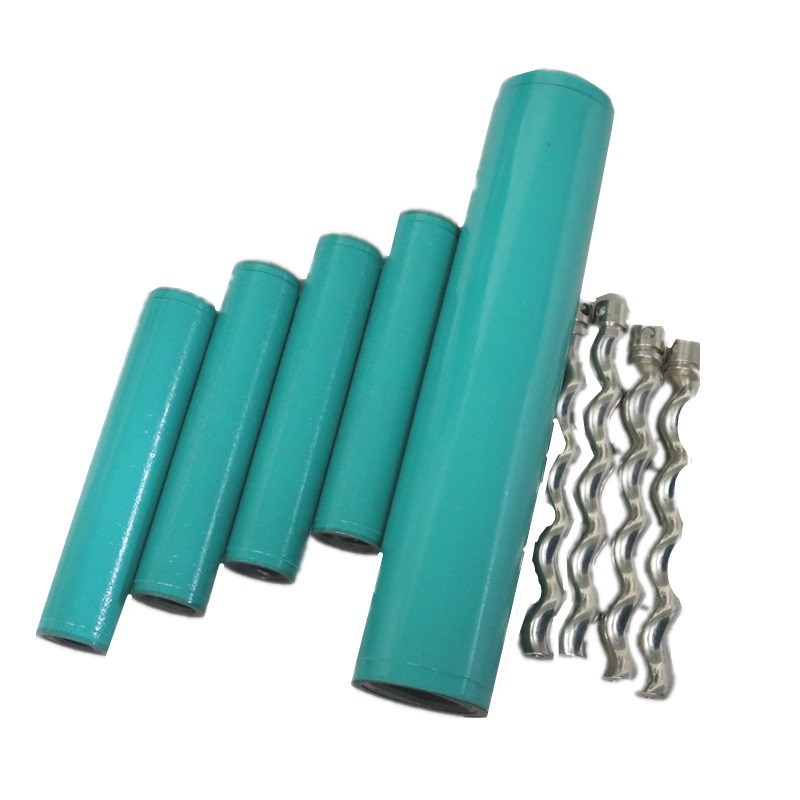

The metal stator with uniform wall thickness is formed with high precision by removing the lining rubber on the basis of the rubber stator with uniform wall thickness and using a special one-time processing technology. In conventional oil production screw pump systems, the rotor is usually made of metal round rods, and the stator is made of a straight shell lined with rubber material.
The stator is usually fixed at the lower end of the oil pipe and is a consumable part. It is inconvenient to disassemble. The oil pipe must be removed when replacing the stator. In order to eliminate this shortcoming, experts proposed to use a screw pump with a metal stator and a plastic rotor. The rotor becomes a consumable part. Since it is connected to the sucker rod, it is more convenient to replace, and there is no need to remove the oil pipe. Its material can be selected from high-hardness rubber, composite materials, etc.

This stator design not only ensures the high delivery efficiency of the NETZSCH NM063BY02S12B screw pump, but also ensures excellent sealing and wear resistance, greatly extending the service life of the pump.
People also ask
Send Your Enquiry :