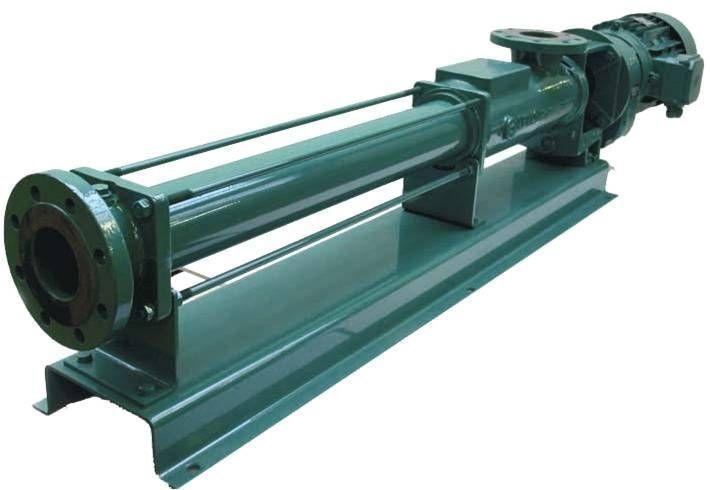
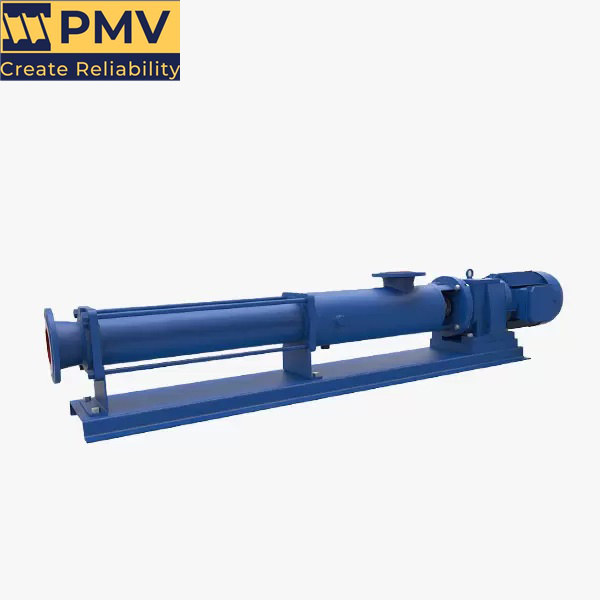
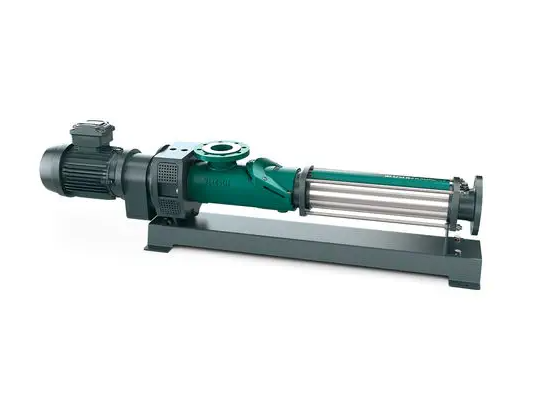
NM021BY01L06B Netzsch
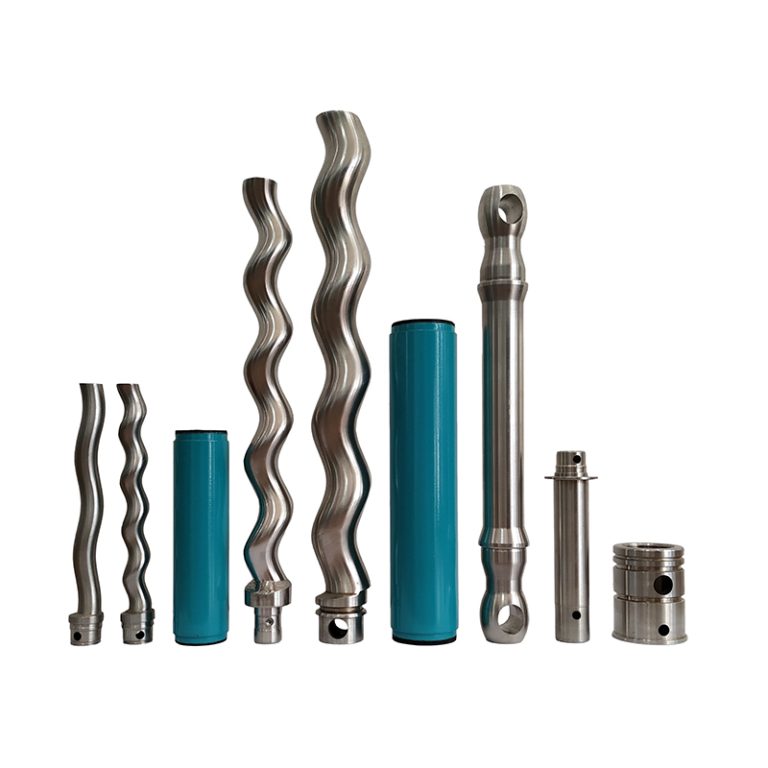
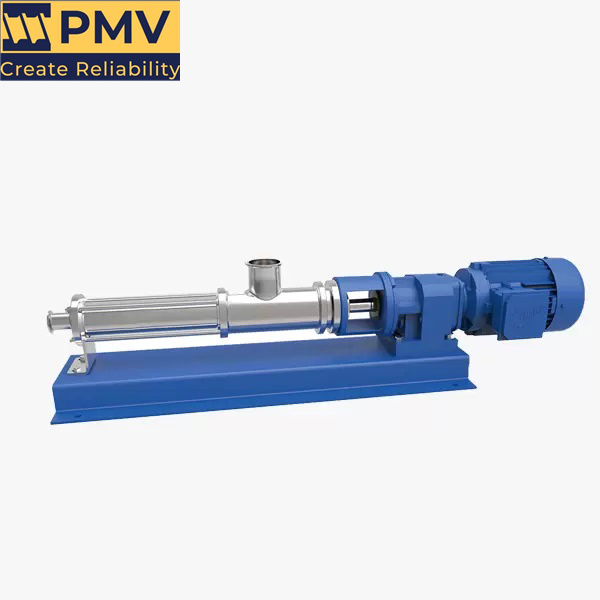
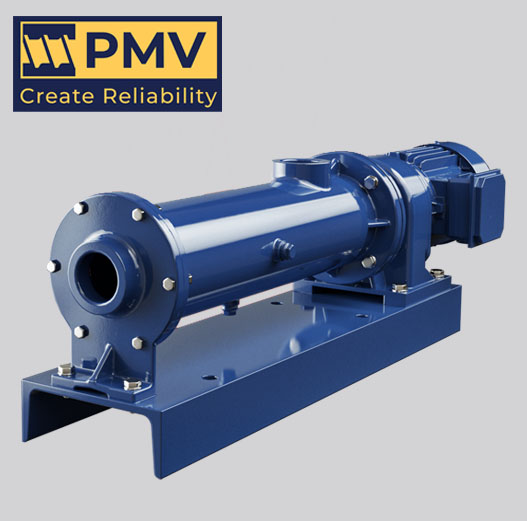
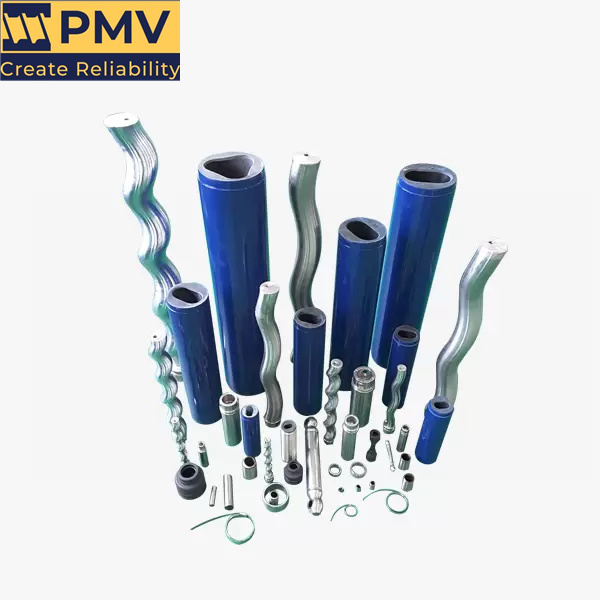
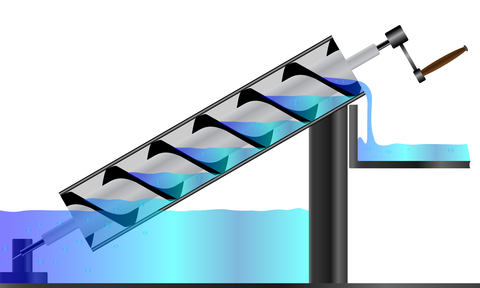
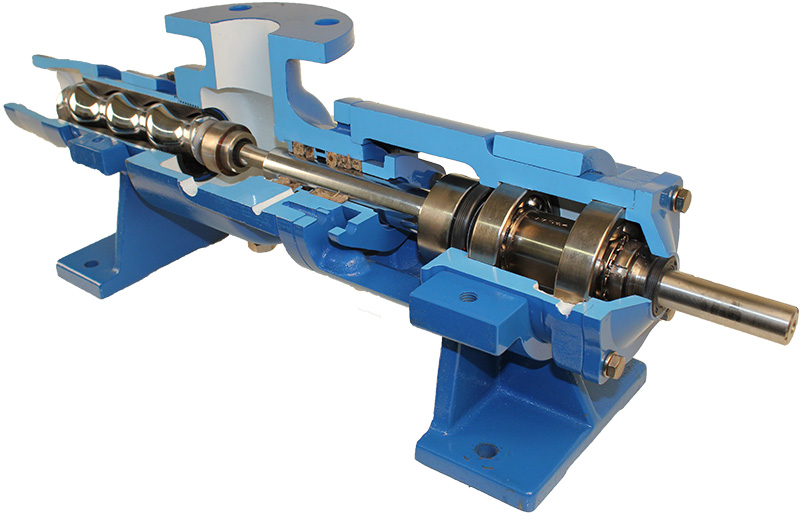
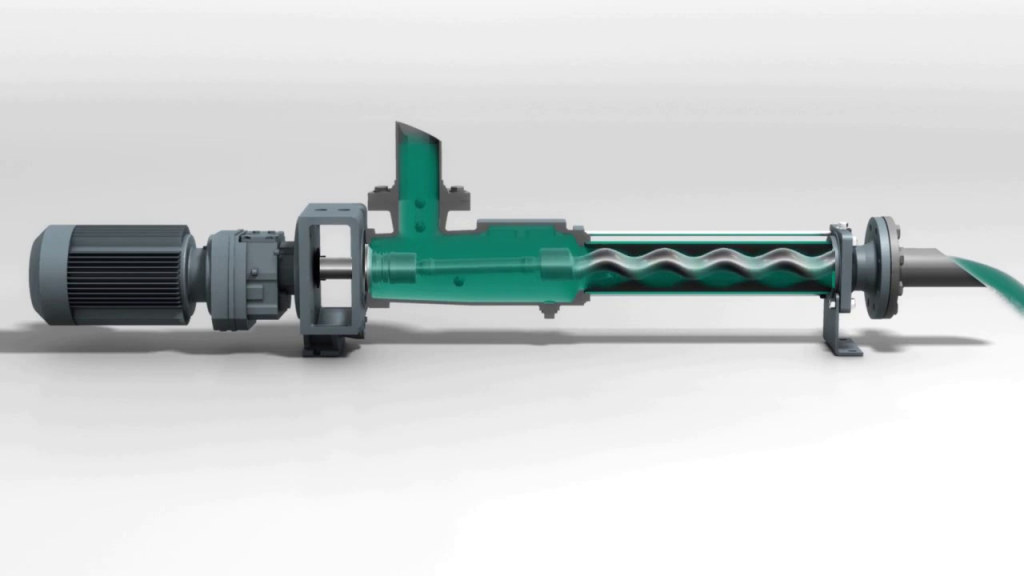
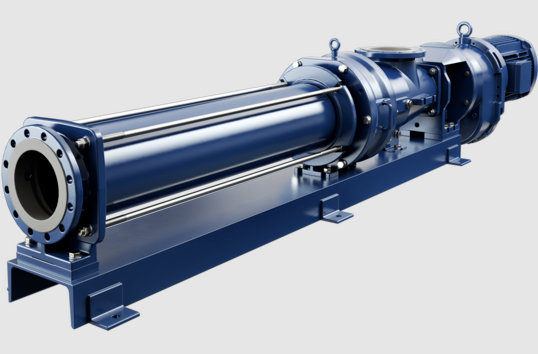
NM021BY01L06B is a high-performance single screw pump, widely used in chemical, pharmaceutical, food and other industries where precise metering and delivery of various fluids are required. Netzsch NM021BY01L06B Progressing Cavity Pump – Precision Design and Superior Performance NM021BY01L06B single screw pump is a high-quality pump product developed by Netzsch for the transportation of high-viscosity fluids….