Food Grade Pump
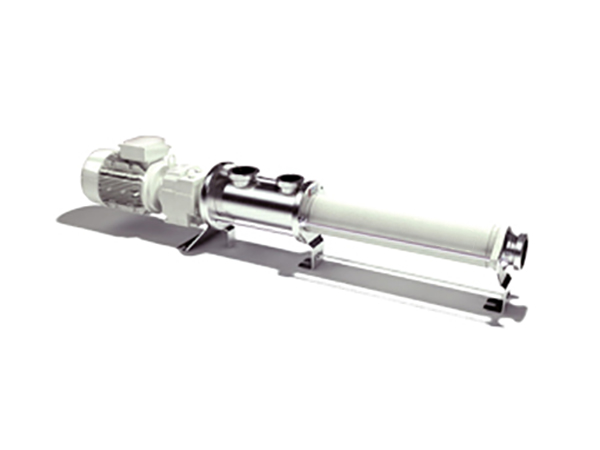
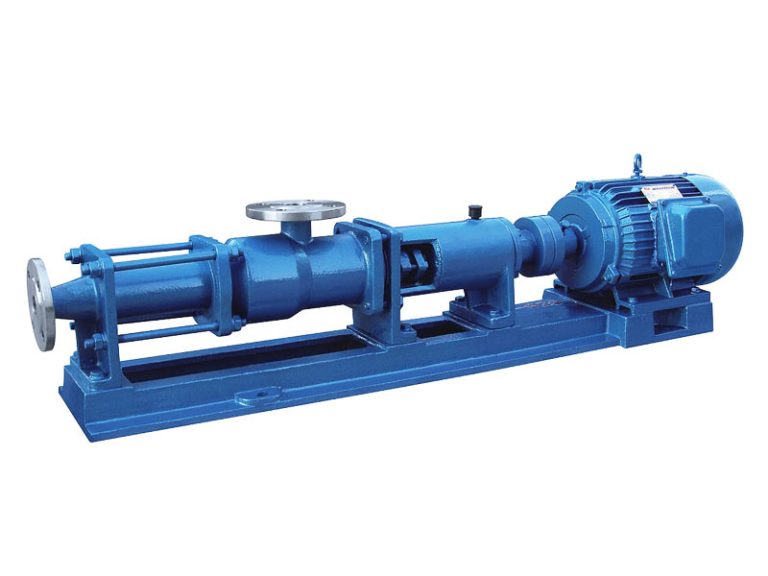
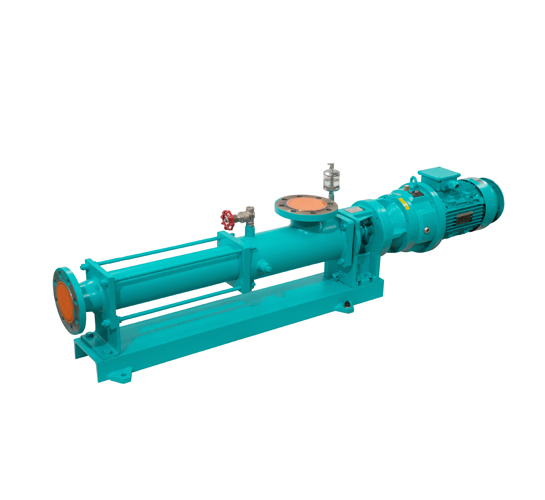
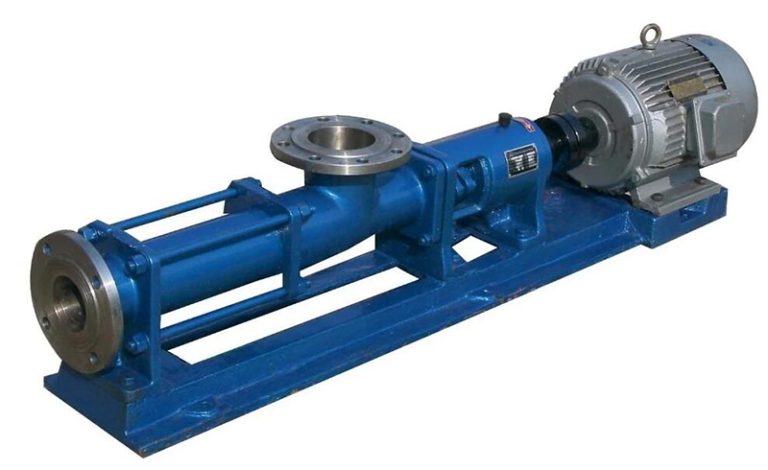
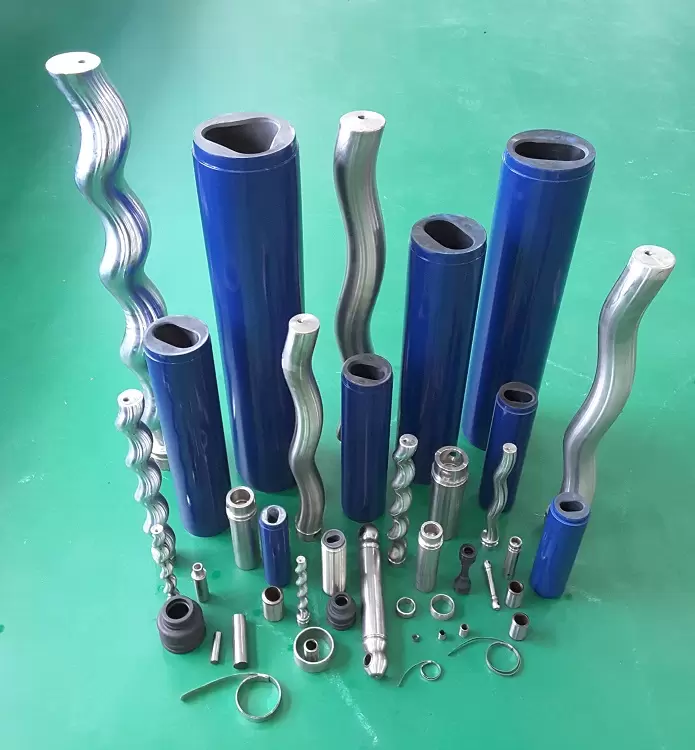
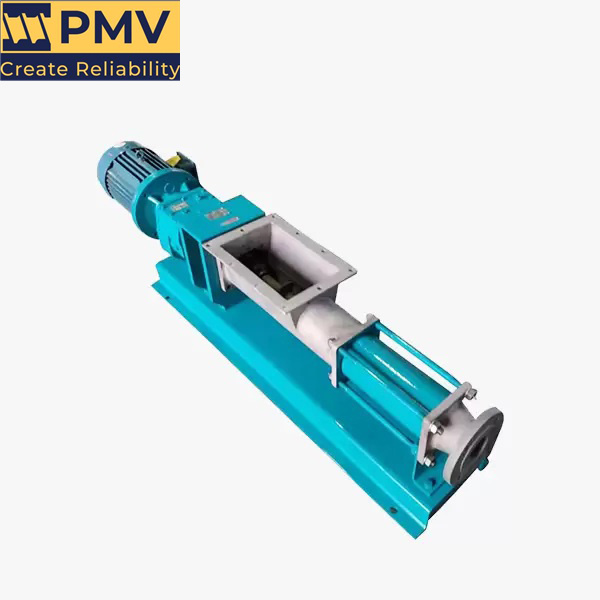
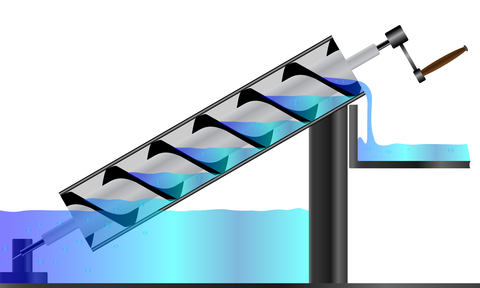
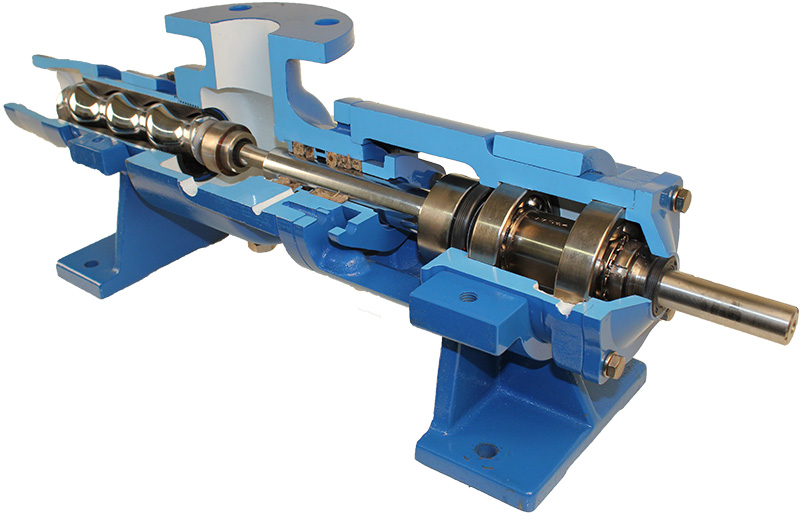
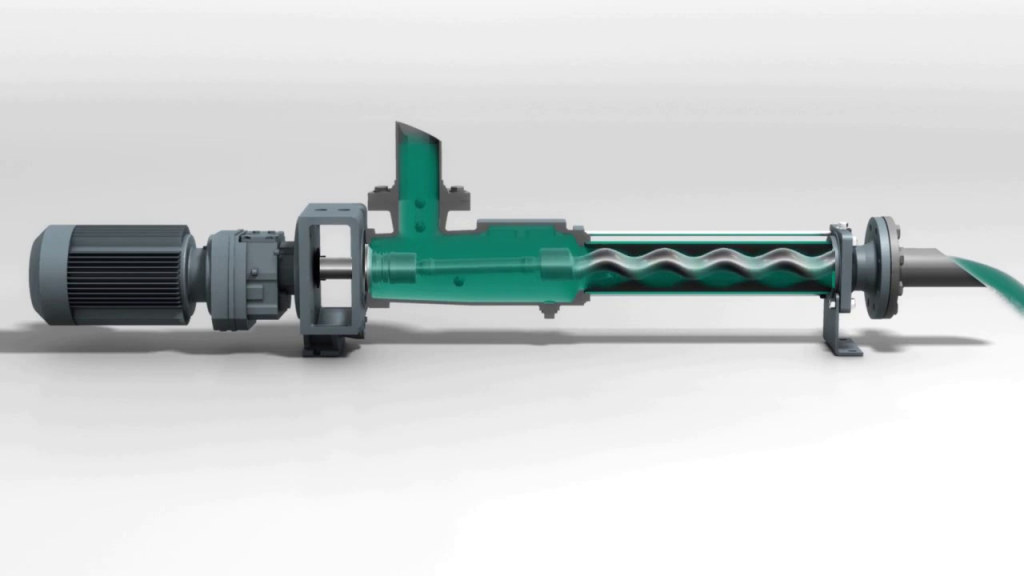
Food Grade Pump Food Grade Pump The PMV™ C is the shortest stainless steel Progressing Cavity Pump in the market. This new Eco designed and compact pump is dedicated for food markets (FDA and European Food regulations compliant materials). Its revolutionary design combines the legendary performance and the reliability of PCM Progressing Cavity Pump technology with…