What is the meaning of API pump?
The American Petroleum Institute
Now, what is an API pump? API pumps meet Standard 610 for General Refinery Service as set by the American Petroleum Institute (API). This U.S. trade association for the oil and natural gas industries develops standards for petroleum and petrochemical equipment.
What is the API standard for gear pumps?
API 676 is the API standard for rotary, positive displacement pumps. The standard provides design criteria for all types of rotary PD pumps. Under the API 676 Standard, there are various codes that define the type of rotary positive displacement pump.
What is the vibration limit of API 676?
Assuming a given capacity, the vibration levels of a PCP are higher than with other API 676 pump types based on concentric motion. A standard PCP may well exceed the limit of 3.8 mm/s (para. 6.11). This low frequency vibration is inherent in the design and not a sign of trouble.
Focus on API 676 compliance
Owing to their operating principle and their roots in waste water treatment, progressive cavity pumps (PCP) typically deviate in several respects from API 676, the petrochemical standard. Some of these deviations can be avoided while others cannot. This article describes what aspects you should pay particular attention to when using a progressive cavity pump.
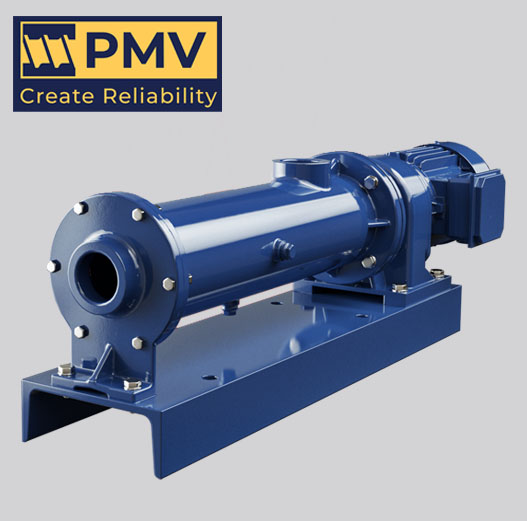
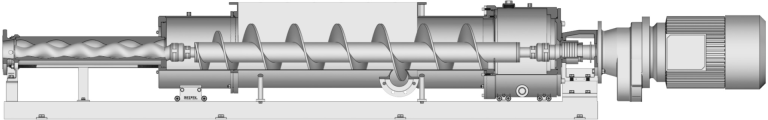
Progressive cavity pumps are positive displacement pumps that handle fluids gently with only minimal shear or turbulence. They are suitable for fluids with very high viscosities and solids contents, no matter how large or abrasive the particles. They can deliver high pressure of 48 bar or more. Even high vapour pressure (low NPSH) or multiphase fluids are not a problem. With their linear curve and low pulsation they are also ideal for dosing applications. Since progressing cavity pumps were originally used in waste water treatment plants (WWTP), their design and production are optimised for this market. However, they can also be employed as a rule in petrochemical applications, though the much higher demands there on pumps can be a problem. Furthermore, the petrochemical industry is based on US standards whereas most PCP manufacturers are located in Europe. The complex measures which are necessary to adapt their standard pumps for use in the petrochemical industry have a dramatic effect on both price and delivery time.
Typical PCP problems
Two issues, in particular, give rise to debates and result in customising, namely the housing and the shaft seal. The typical PCP cast housings frequently fail to meet the requirements of US standards:
PCPs typically have articulated rotor joints to allow for the eccentric rotor movement. A rotor with such joints comes with assembly restrictions that are not compatible with an API 682 mechanical seal. At best, a heavily engineered seal in the spirit of API 682 is possible. PCP vendors generally use universal cartridge seals adapted to the pump’s dimensional restrictions.
Advantages of PCPs
PCPs typically operate at slow speed (100 to 300 min-1) – about 10 to 20 % compared to a centrifugal pump. There is therefore no need for exact alignment or balancing and the baseplates can normally manage without precision machined pads and jacking screws.
The shaft bearings of PCPs are grease lubricated and typically sealed for life. An oil lubrication system requiring monitoring and cooling can be dispensed with. It is common practice to do without dedicated shaft bearings altogether and use the gearbox bearings instead to support the shaft – these so-called block pumps also have no coupling. The shaft seals produce virtually no frictional heat. Seal cooling is rarely needed and the standard seal plans offered by PCP vendors often omit the cooler stipulated by API 682.
References to other US standards
Finally, there are references to other US standards, for example regarding gearboxes, bearings and welding. API 676 references AGMA (American Gear Manufacturers Association) and ABMA (American Bearing Manufacturers Association) standards and requires gearboxes to conform to AGMA 6010 or even API 677. However, no API 677 gears are available for a PCP’s ratings and drive configuration. The AGMA and ABMA standards are not used outside America. European gear manufacturers design and calculate according to DIN 3990 or ISO 6336.
For structural welding, API 676 references AWS D1.1 (American Welding Society). Yet once again, welding to AWS is unusual in Europe and hardly ever available. Structural parts are mainly welded according to ISO.
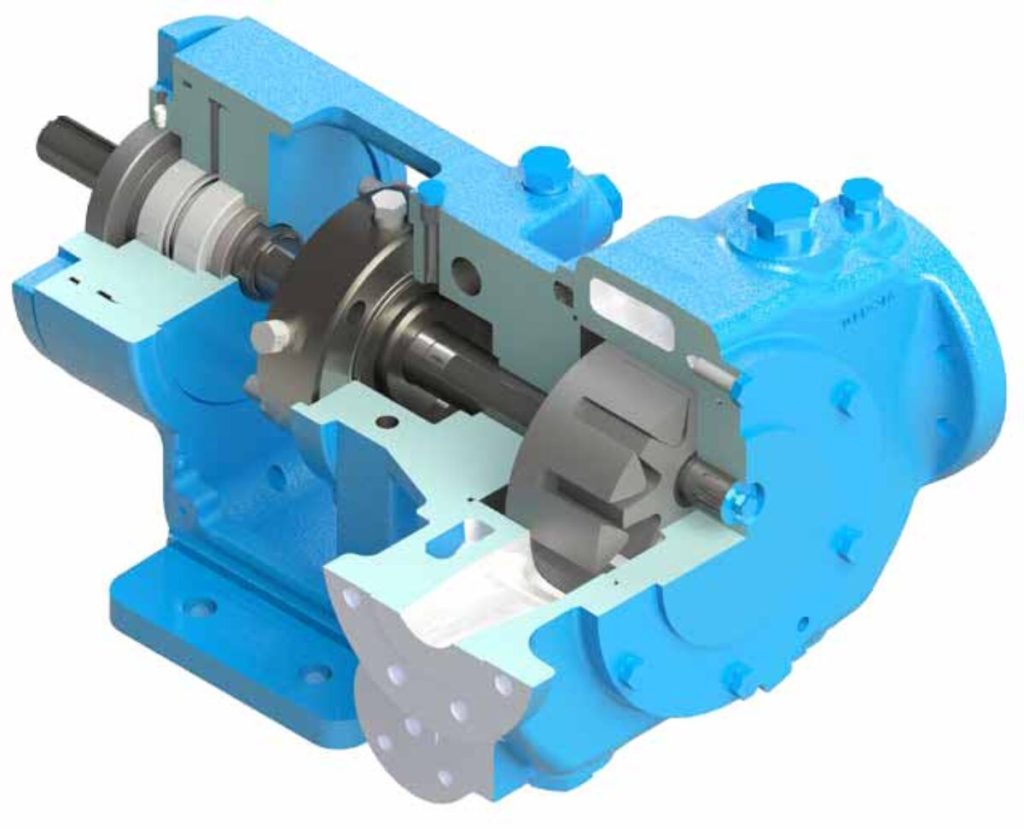
Overview. The Viking API 676 Series are foot-mounted internal gear pumps, designed and manufactured to comply fully with the current version of American Petroleum Institute’s design standard for positive displacement pumps, API 676.
Fill up and submit the below inquiry form, or directly write us an email: info@pumpvv.com