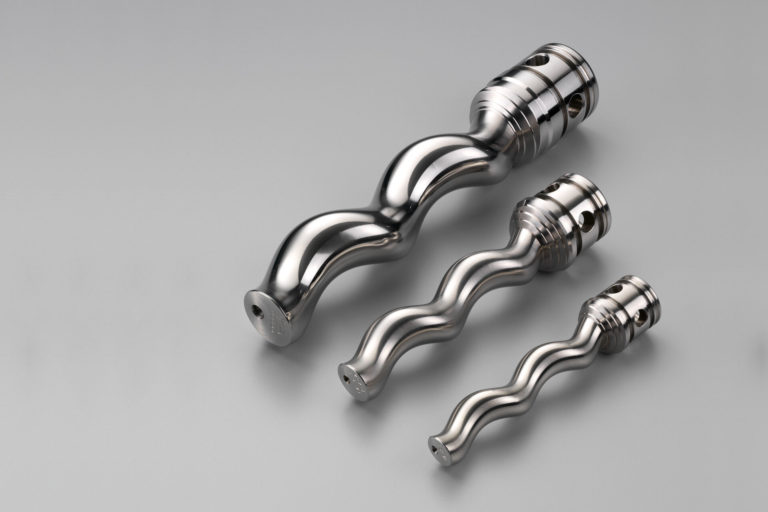
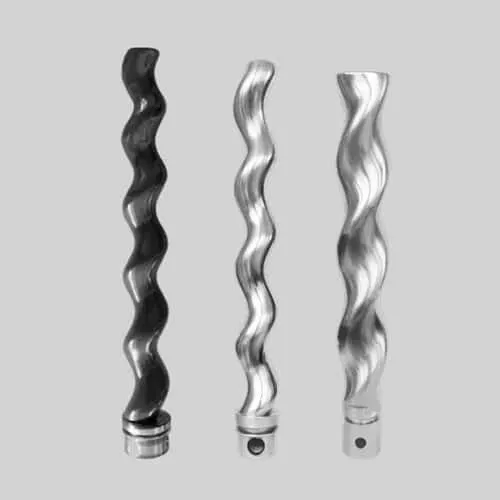
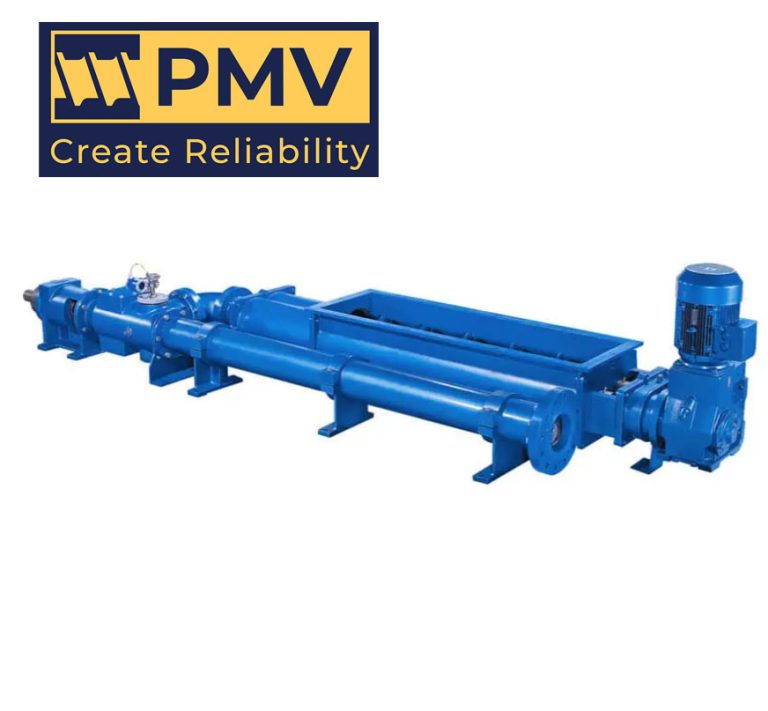
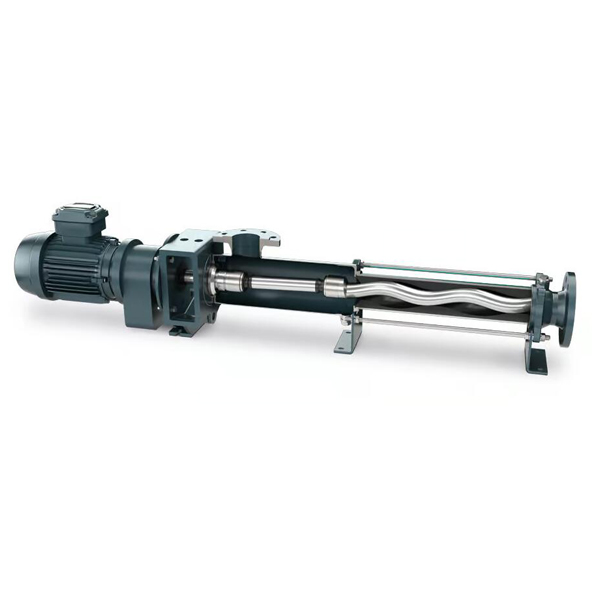
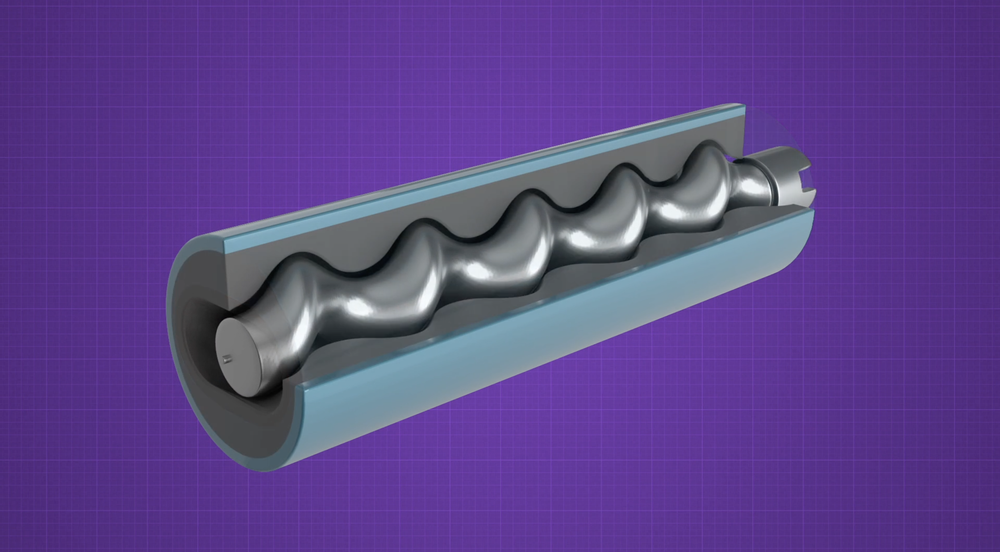
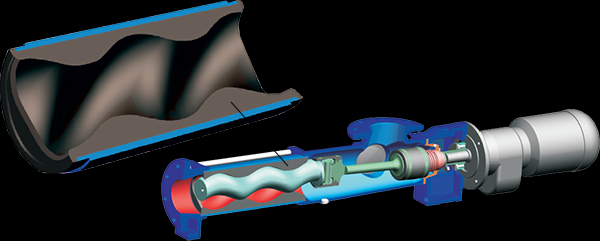
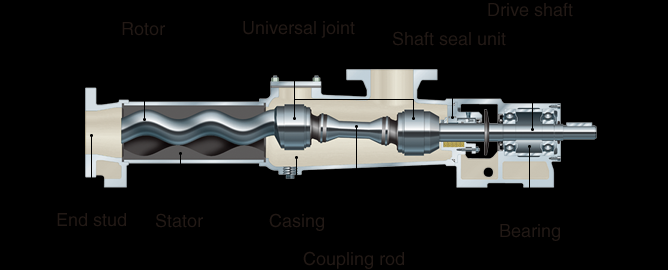
What is Api 676 Pump?
What is the meaning of API pump? The American Petroleum Institute Now, what is an API pump? API pumps meet Standard 610 for General Refinery Service as set by the American Petroleum Institute (API). This U.S. trade association for the oil and natural gas industries develops standards for petroleum and petrochemical equipment. What is the…